Tutorials
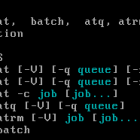
Although CronTabs are useful, sometimes you just want to run a command at a given time once and not have it reoccurring. The commands `at` and `batch` can do just that. The `at` command can be used to run a command based on a specific time. Lets say you wanted to run a command 1 day in advance or even 1 hour from your current time, `at` would be the tool to use. `batch` on the other […]
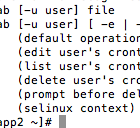
Setting up linux crontabs is alot easier then it appears. In order to setup linux crontabs successfully you need to understand how the units of time work. Here is a table in the order of priority from top to bottom with a break down of the values you can use. minute (0 – 59) hour (0 – 23) day of the month (1 – 31) month (1 – 12) OR jan, feb, mar, apr… day of the […]
Disabling direct root ssh access to your GNU/Linux Box is great for security, but sometimes you just want to be able to directly login via root without that restriction. You can disable or enable it by doing the following: First open your /etc/ssh/sshd_config in a editor. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Next you will find a line that has permitrootlogin and it is either set to yes or no. To enable direct root access set the value to yes like […]
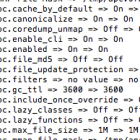
In order to enable slow query logs for MySQL on your system you would need to do the following. 1st Step is to edit your my.cnf file which is located in your /etc directory. vi /etc/my.cnf Once you have your my.cnf file open, then add the following 4 lines then save and exit the file. [mysqld] log-slow-queries log-slow-queries=/var/log/mysql/slow-queries.log long_query_time=1 Then create the file slow-queries.log. You can have the file in any spot you wish, as long as […]
Below are the steps needed in order to successfully install the PHP APC optimizer module on Red Hat based systems such as CentOS. Before installing PHP APC, we need to start by installing the php pear module, php-devel, httpd-devel, and pcre-devel modules. yum install php-pear php-devel httpd-devel pcre-devel After you install the required packages, then we can go ahead and install PHP APC. In the command line type the following: pecl install apc PHP APC will now […]
HTML and CSS - October 13, 2011
Find examples on how to modify your CSS code in order to get things to display properly in each version of Internet Explorer.
Linux Video Tutorials - August 15, 2011
This video discusses how you can create logical volumes using LVM using pvcreate, vgcreate, lvcreate, lvresize, lvrename, mkfs, and resize2fs.
Using the ab utility you are able to test your current version of apache and how well it performs to multiple requests for even a set amount of time. It’s not hard at all to use this utility. All you need to do is the following: ab –n 100 –c 10 http://domain_to_test_with_ab.com/index.php What we’re doing above is sending 100 requests to the index.php file of that domain in increments of 10. This means that site will receive […]
In order to change the default time zone for your machine all you would need to do is follow a few simple steps. First thing you need to know is where your default time zone is actually set. The path to that file is as follows: /etc/localtime To find a list of the available time zones you could look in: /usr/share/zoneinfo So now that we know those basic details, lets continue on to modifying our time zone. […]
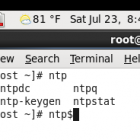
Configure NTP (Network Time Protocol) to synchronize your system clock on Red Hat Based GNU/Linux Systems. NTP allows you to easily synchronize your server time with a specified server. Below are the steps to easily configure this service. Step 1: Install the NTP utility yum –y install ntp Step 2: Synchronize your server/computer with the specified server ntpdate pool.ntp.org Step 3: Start the ntpd service service ntpd start Step 4: Enable the service to auto start on boot […]









Follow DevBlog.co on Twitter
follow us on Twitter
Join DevBlog.co is on Facebook!
DevBlog.co on Facebook
Follow DevBlog.co on Digg!
DevBlog.co on Digg